一、前言
本系列文章为《剑指Offer》刷题笔记。
刷题平台:牛客网
书籍下载:共享资源
二、题目
1、思路
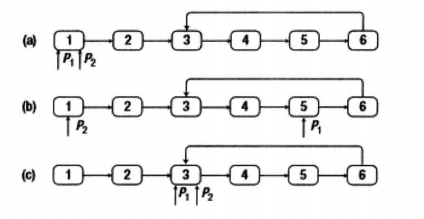
可以用两个指针来解决这个问题。先定义两个指针P1和P2指向链表的头结点。如果链表中的环有n个结点,指针P1先在链表上向前移动n步,然后两个指针以相同的速度向前移动。当第二个指针指向的入口结点时,第一个指针已经围绕着揍了一圈又回到了入口结点。
以下图为例,指针P1和P2在初始化时都指向链表的头结点。由于环中有4个结点,指针P1先在链表上向前移动4步。接下来两个指针以相同的速度在链表上向前移动,直到它们相遇。它们相遇的结点正好是环的入口结点。
现在,关键问题在于怎么知道环中有几个结点呢?
可以使用快慢指针,一个每次走一步,一个每次走两步。如果两个指针相遇,表明链表中存在环,并且两个指针相遇的结点一定在环中。
随后,我们就从相遇的这个环中结点出发,一边继续向前移动一边计数,当再次回到这个结点时,就可以得到环中结点数目了。
2、代码
C++:
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead)
{
if(pHead == NULL){
return NULL;
}
ListNode* meetingnode = MeetingNode(pHead);
if(meetingnode == NULL){
return NULL;
}
// 回环链表结点个数
int nodesloop = 1;
// 找到环中结点个数
ListNode* pNode1 = meetingnode;
while(pNode1->next != meetingnode){
pNode1 = pNode1->next;
nodesloop++;
}
pNode1 = pHead;
// 第一个指针向前移动nodesloop步
for(int i = 0; i < nodesloop; i++){
pNode1 = pNode1->next;
}
// 两个指针同时移动,找到环入口
ListNode* pNode2 = pHead;
while(pNode1 != pNode2){
pNode1 = pNode1->next;
pNode2 = pNode2->next;
}
return pNode1;
}
private:
// 使用快慢指针,找到任意的一个环中结点
ListNode* MeetingNode(ListNode* pHead){
ListNode* pSlow = pHead->next;
if(pSlow == NULL){
return NULL;
}
ListNode* pFast = pSlow->next;
while(pFast != NULL && pSlow != NULL){
if(pFast == pSlow){
return pFast;
}
pSlow = pSlow->next;
pFast = pFast->next;
if(pFast != NULL){
pFast = pFast->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
Python:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
# write code here
if pHead == None:
return None
meetingnode = self.MeetingNode(pHead)
if meetingnode == None:
return None
nodeslop = 1
node1 = meetingnode
while node1.next != meetingnode:
node1 = node1.next
nodeslop += 1
node1 = pHead
for _ in range(nodeslop):
node1 = node1.next
node2 = pHead
while node1 != node2:
node1 = node1.next
node2 = node2.next
return node1
def MeetingNode(self, pHead):
slow = pHead.next
if slow == None:
return None
fast = slow.next
while fast != None and slow != None:
if slow == fast:
return fast
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
if fast != None:
fast = fast.next
return None
来源:
https://cuijiahua.com/blog/2018/01/basis_55.html