一、前言
简单选择排序是一种选择排序。
选择排序:每趟从待排序的记录中选出关键字最小的记录,顺序放在已排序的记录序列末尾,直到全部排序结束为止。
二、算法思想
简单排序很简单,它的大致处理流程为:
- 从待排序序列中,找到关键字最小的元素;
- 如果最小元素不是待排序序列的第一个元素,将其和第一个元素互换;
- 从余下的 N – 1 个元素中,找出关键字最小的元素,重复(1)、(2)步,直到排序结束。
动态效果示意图:
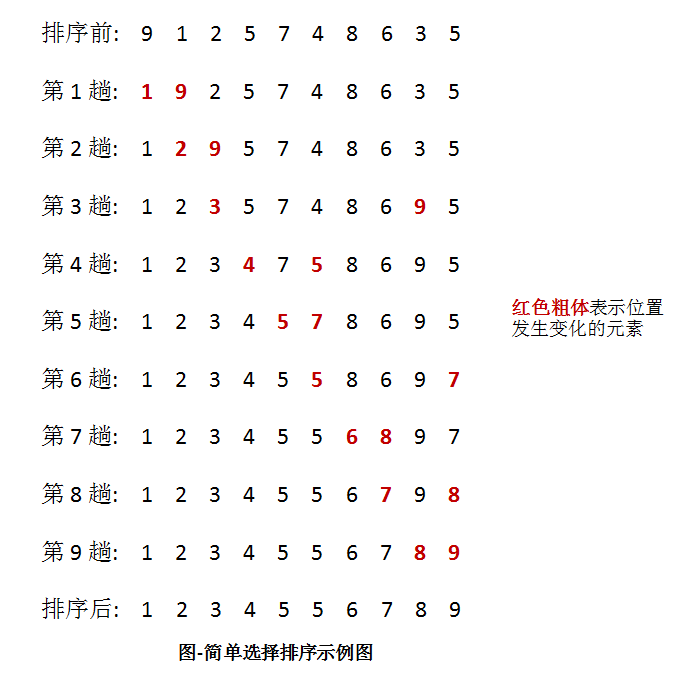
举例说明,处理过程示意图如下所示:
如图所示,每趟排序中,将当前第 i 小的元素放在位置 i 上。
1、代码
C++:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 简单选择排序
vector<int> SelectSort(vector<int> list){
// 需要遍历获得最小值的次数
// 要注意一点,当要排序 N 个数,已经经过 N-1 次遍历后,已经是有序数列
vector<int> result = list;
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
// 用来保存最小值得索引
int index = i;
// 用来保存最小值得索引
for (int j = i + 1; j < result.size(); j++){
if (result[index] > result[j]){
index = j;
}
}
if (index == i){
continue;
}
// 将找到的第i个小的数值放在第i个位置上
swap(result[i], result[index]);
cout << "第" << i + 1<< "趟:\t";
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return result;
}
void main(){
int arr[] = { 6, 4, 8, 9, 2, 3, 1 };
vector<int> test(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
cout << "排序前" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < test.size(); i++){
cout << test[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int> result;
result = SelectSort(test);
cout << "排序后" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
}
运行结果:
Python:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
def SelectSort(input_list):
'''
函数说明:简单选择排序(升序)
Author:
www.cuijiahua.com
Parameters:
input_list - 待排序列表
Returns:
sorted_list - 升序排序好的列表
'''
if len(input_list) == 0:
return []
sorted_list = input_list
length = len(sorted_list)
for i in range(length):
min_index = i
for j in range(i + 1, length):
if sorted_list[min_index] > sorted_list[j]:
min_index = j
if min_index == i:
continue
temp = sorted_list[i]
sorted_list[i] = sorted_list[min_index]
sorted_list[min_index] = temp
return sorted_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
input_list = [6, 4, 8, 9, 2, 3, 1]
print('排序前:', input_list)
sorted_list = SelectSort(input_list)
print('排序后:', sorted_list)
运行结果同上。
三、算法分析
1、简单算法排序性能
其中,N2为N^2。
2、时间复杂度
简单选择排序的比较次数与序列的初始排序无关。 假设待排序的序列有 N 个元素,则比较次数总是N (N – 1) / 2。
而移动次数与序列的初始排序有关。当序列正序时,移动次数最少,为 0.
当序列反序时,移动次数最多,为3N (N – 1) / 2。
所以,综合以上,简单排序的时间复杂度为 O(N^2)。
3、空间复杂度
简单选择排序需要占用 1 个临时空间,用于保存最小值得索引。
本站整理自:
http://www.cnblogs.com/jingmoxukong/p/4303289.html
来源:
https://cuijiahua.com/blog/2017/12/algorithm_5.html